Title: Wykorzystanie warstw konwerterów energii w nowych rozwiązaniach dla ogniw fotowoltaicznych.
English title: Energy converting layers in new solutions for photovoltaic cells
Comment: Agreement No.: UMO-2016/21/D/ST7/01215 for the research project 2016/21/D/ST7/01215
Implementation: start: 25/01/2017 end: 24/01/2020
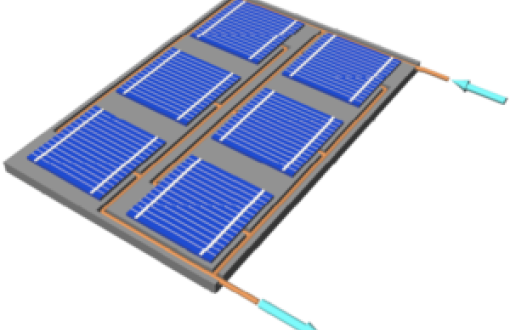
Description: The scientific goal of the project is to study the impact of the use of layers containing ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) on the course of photoelectric phenomena in solar cells, and in particular on the efficiency of photovoltaic (PV) conversion in these structures. The introduction of layers of ZnO nanoparticles into the photovoltaic structure is aimed at down conversion, thanks to which high-energy (UV) photons are converted into low-energy photons (visible light), used more effectively in photovoltaic conversion. The project provides for the design and implementation of test structures of solar cells containing layers of NPs ZnO converters in various photovoltaic structures, taking into account the silicon polycrystalline p-n structure as the basic one. The tests of the proposed structures will be part of the verification of the hypothesis on the suitability of selected solutions of NPs ZnO layers as energy converters for applications in solar cells, in order to improve the efficiency of photoconversion.
Title: ProeTEX: MicroNanoStructured fiber systems for Emergency-Disaster Wear
Comment: Project implemented as part of the Lodz University of Technology team led by prof. Izabella Krucińska.
Implementation: 2005 – 2010
Description: The participation of the Department of Semiconductor and Optoelectronic Devices in the Protection e-Textiles - ProeTEX program consisted in designing, manufacturing and testing innovative temperature sensors with a textronic structure, intended for integration with firefighter protective clothing. In the first stage of the project, these works concerned the implementation of a temperature monitoring system for the test rescue suit using a commercial digital temperature sensor system. As a result of this work, a flexible thermal conductive sheath for digital temperature sensors placed in the fabric was designed and tested. The results of these studies were used to develop improved versions of the temperature measurement system, based on sensors with serial data transmission and increased measurement accuracy. As part of the research, a technique for making laser microwelds for connecting such systems was also developed.
A separate part of the research was the development of an analog, fully testronic temperature sensor with high flexibility. Such a device has been implemented and will be used to directly incorporate the measurement systems into the structure of the fabric by using standard knitting techniques for their production.
Title: POLONIUM 2012-2013: Nowe rozwiązania konwerterów energii dla ogniw słonecznych.
Commentary: Polish-French POLONIUM personal exchange program for 2012-2013
Implementation: 2012-2013
Description: The aim of the project is to use a new solar radiation capture solution to improve the efficiency of silicon photovoltaic cells by expanding their photoconversion spectrum. The project proposes the use of a nanoparticle ZnO (NPs) layer as a down converter placed near the solar cell emitter in order to improve the external quantum efficiency and photoconversion efficiency of silicon cells. Preliminary research conducted at the Lyon Institute of Nanotechnology (INL) showed the great potential of ZnO nanoaggregates as photon energy converters. It was noticed that the high purity of the nanoparticle ZnO crystal leads to the disappearance of luminescence emission in the visible range. For this reason, in order to increase the emission in the green and red light range, oxygen defects were introduced into the ZnO NPs structure, obtaining a material ideal for the construction of down-conv layers
Title: GECCO: 3D struktury GaN dla wysokowydajnych półprzewodnikowych źródeł światła
Comment: 7th Framework Programme
Implementation: 2012-2015
Description: Semiconductor light sources, currently based on gallium nitride (GaN), are expected to replace inefficient and environmentally unfriendly conventional light sources, significantly contributing to energy savings. To achieve this, it is necessary to develop white light-emitting diodes (LEDs) with greater efficiency and lower cost per lumen emitted. In the project, a new concept of 3D structures was proposed and tested. The new solution will introduce the development of semiconductor light sources to a completely new level of efficiency compared to LED structures made in conventional 2D technology, based on planar thin-film technology.
The team from the Lodz University of Technology participates mainly in the work related to the modeling of the new concept of diode structures at various stages of its evaluation. More information on the project website: GECCO.
Title: branie strażackie nowej generacji z tekstronicznym systemem monitorowania parametrów fizjologicznych
Comment: Project implemented as part of the Lodz University of Technology team under the supervision of prof. dr hab. Izabella Krucińska
Implementation: 2006-2008
Description: The project was implemented by the Lodz University of Technology (Faculty of Materials Technology and Textile Design and the Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Electronics, Computer Science and Automation), ARLEN clothing company and the Central Institute for Labor Protection of the National Research Institute. As part of the project, a firefighter's suit with a textronic system for monitoring skin temperature, temperature under clothing, external temperature, firefighter's heart rate and characteristics of his movement was developed.